Organising an event on the scale of UEFA EURO 2016 is an environmental challenge, thus the organisation of the event started in 2014.
Each of the organisational domains involved in the tournament (including transport, logistics, lighting, catering, merchandising and broadcasting) will have a wide range of direct and indirect environmental impacts, in terms of air pollution, consumption of natural resources and contribution to climate change.
These are challenges that UEFA takes seriously. UEFA has committed to reducing its environmental impact by taking a realistic step-by-step approach, with the objective of continuously improving its environmental performance.
Close cooperation with all tournament stakeholders (EURO 2016 SAS, the French state, the ten host cities, partners and suppliers, associations and supporters) and a thorough analysis of the material issues have provided the basis for UEFA’s environmental sustainability strategy.
An initial environmental impact assessment has already been conducted to identify which activities contribute the most so that the organisers can work with stakeholders to define and implement concrete action plans to mitigate these effects.
Four environmental priorities have been set:
Transport is a major contributor to any event’s carbon footprint and as such it is an important focal point in the EURO 2016 sustainability strategy. By promoting the use of public transport, UEFA aims to leave a positive legacy in this field for the host country and the host cities.
Fans will be offered various transport services to help them get to and from the stadiums and fan zones during the tournament. UEFA is working closely with its partners at national, regional and local level to ensure an efficient public transport system is in place, while incorporating aspects of eco-mobility and taking into consideration air quality, energy and environmental impact.
The UEFA EURO 2016 Eco-calculator
With the help of Climate Friendly, UEFA has developed the UEFA EURO 2016 eco-calculator. This online tool enables fans to find out how their journeys to the tournament will contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and encourages them to offset their emissions.
For its part, UEFA and its staff working on EURO 2016 are reducing their carbon footprint by travelling by train whenever possible (e.g. between UEFA headquarters in Nyon, Switzerland, and the EURO 2016 SAS offices in Paris, France).
For longer distances, where air travel is more appropriate, the emissions from all official UEFA flights, including staff travel for other UEFA competitions, are offset through Climate Friendly, a leading international carbon reduction and offset organisation. Moreover, all meeting rooms at UEFA headquarters and EURO 2016 SAS are equipped with videoconferencing solutions, reducing the need to travel for meetings.
Waste management
Waste management follows the 3Rs approach: reduce, reuse and recycle. The objectives, as defined in the UEFA EURO 2016 Waste Management Vision, are to achieve a 50% recycling rate, zero waste to landfill and greater public awareness.
Initiatives in this field range from using reusable cups and working towards dematerialisation (reduction of printed documents) to using less packaging, reusing materials for other events and donating surpluses.
With 24 participating national teams, EURO 2016 is an opportunity not only to leave a legacy for the host country, but also to share good practices and messages about recycling and waste management with fans from all around the world.
Energy and water
Many French stadiums already use renewable energy such as solar, wind and geothermal energy. Rainwater is also collected in most stadiums and is reused for pitch watering, for example.
In addition, UEFA’s strategy is to reduce energy consumption by identifying the realistic needs of the stakeholders and designing tailored action. This will include, for instance, using generators equipped with diesel particulate filters and ensuring electric equipment is optimised.
Sourcing of products and services
To encourage the responsible sourcing of products and services, UEFA has produced a sustainable sourcing guide and included a sustainability addendum in all operational tender procedures, procurement processes and contracts related to EURO 2016.
www.uefa.com










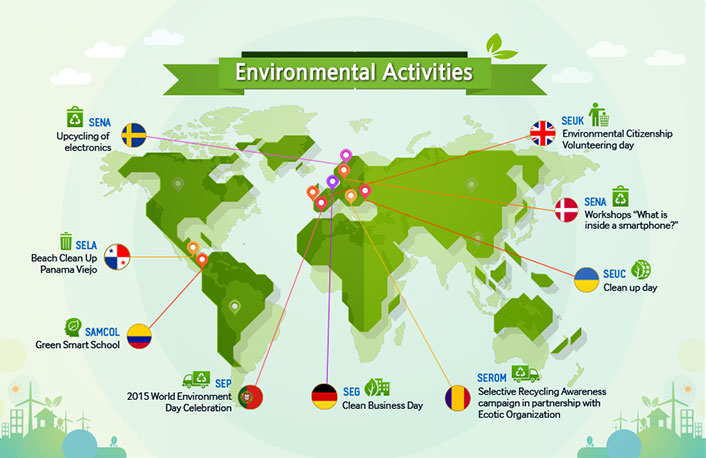
 As the planet faces a growing list of problems, from climate change and pollution to environmental degradation and resource depletion, the preservation and conservation of the environment has never been more significant.
As the planet faces a growing list of problems, from climate change and pollution to environmental degradation and resource depletion, the preservation and conservation of the environment has never been more significant.

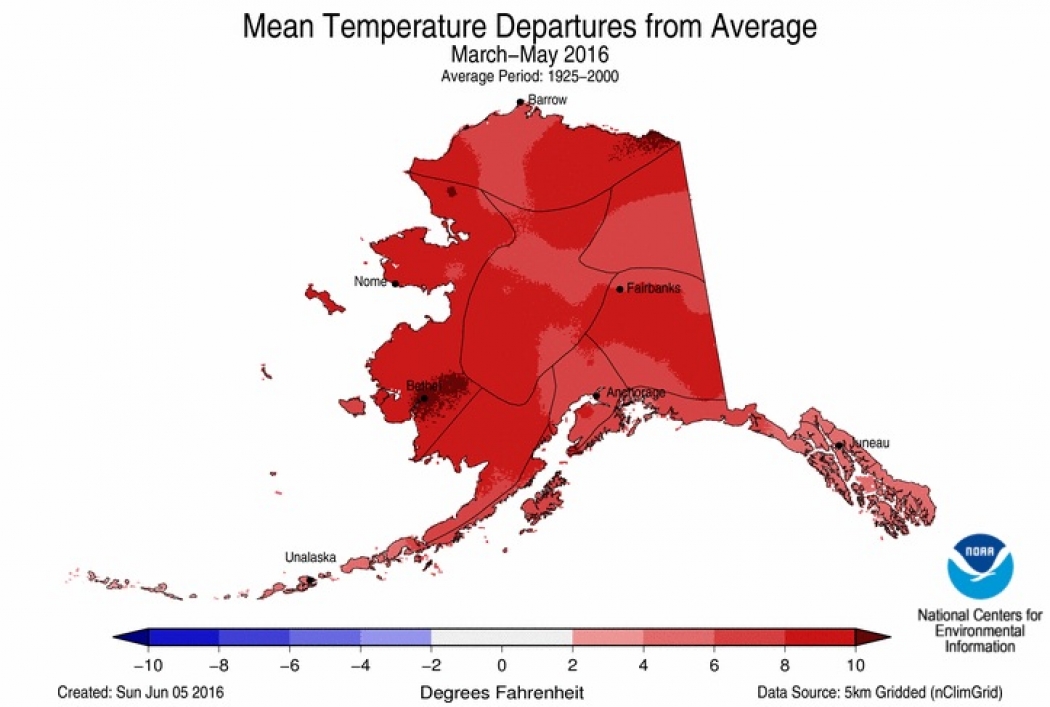
 Alaska just can’t seem to shake the fever it has been running. This spring was easily the hottest the state has ever recorded and it contributed to a year-to-date temperature that is more than 10°F (5.5°C) above average, according to data released by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Alaska just can’t seem to shake the fever it has been running. This spring was easily the hottest the state has ever recorded and it contributed to a year-to-date temperature that is more than 10°F (5.5°C) above average, according to data released by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.


 ABB today commissioned an integrated solar-diesel microgrid installation at its 96,000 square meter Longmeadow facility in Johannesburg, South Africa. This is a world premiere for the innovative solution with fully grid-connected and off-grid functionalities designed to maximize the use of renewable energy and ensure uninterrupted power supply to keep the lights on and the factories running during any planned or unplanned power outages on the main grid supply.
ABB today commissioned an integrated solar-diesel microgrid installation at its 96,000 square meter Longmeadow facility in Johannesburg, South Africa. This is a world premiere for the innovative solution with fully grid-connected and off-grid functionalities designed to maximize the use of renewable energy and ensure uninterrupted power supply to keep the lights on and the factories running during any planned or unplanned power outages on the main grid supply.
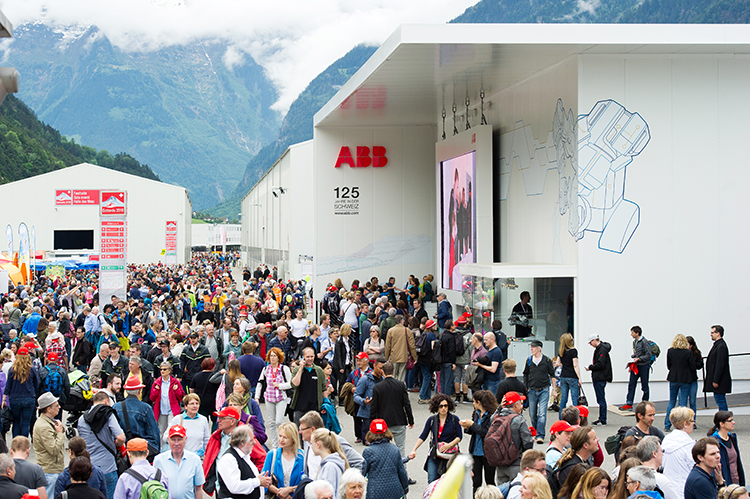




 Update – 80,000 visitors joined in the festivities during the public days on June 4 and 5, 20,000 of whom visited ABB’s special technology pavilions
Update – 80,000 visitors joined in the festivities during the public days on June 4 and 5, 20,000 of whom visited ABB’s special technology pavilions




