 The Prime Ministers of Sweden and Serbia confirmed that IKEA will invest 300 million euros in Serbia by the end of the year at the World Economic Forum in Davos during January. Exclusively for Energy portal Mrs Irena Dobosz, the manager for sustainability at IKEA company for Southeast Europe, has said something more about the way in which this company operates. IKEA follows the values and the concept of the founder Ingvar Kampard, who grew up in Smaland province in Sweden. Rocky landscape dominates Smaland province, and residents have the reputation of innovative people because they use all raw materials in a thoughtful way and do not recognise imperfect solutions. That spirit which is characterized by the belief that no method is more effective than the good example is incorporated in IKEA.
The Prime Ministers of Sweden and Serbia confirmed that IKEA will invest 300 million euros in Serbia by the end of the year at the World Economic Forum in Davos during January. Exclusively for Energy portal Mrs Irena Dobosz, the manager for sustainability at IKEA company for Southeast Europe, has said something more about the way in which this company operates. IKEA follows the values and the concept of the founder Ingvar Kampard, who grew up in Smaland province in Sweden. Rocky landscape dominates Smaland province, and residents have the reputation of innovative people because they use all raw materials in a thoughtful way and do not recognise imperfect solutions. That spirit which is characterized by the belief that no method is more effective than the good example is incorporated in IKEA.
EP: IKEA is soon coming to the Serbian market. It is a renowned company which invests a lot in recycling, in environmental protection and in well-selected raw materials. Tell us something more about the practice which IKEA implements world-wide. How did it become so successful and popular in your opinion?
Irena Dobosz: One of the basic developmental principles of the IKEA company is sustainable development and we participate and support a large number of global initiatives that deal with this issue. In accordance with our concept of “democratic design” all of our products must meet this component and they are made of recycled materials or materials from renewable sources or they can be recycled. We invest significant resources and efforts in our own renewable energy sources. The wood that we use is certified and it is from renewable sources, as well as coffee, fish and seafood which are served in our restaurants. Similar efforts are being made when it comes to cotton. All the cotton used for our products comes from a few sustainable sources, which means that the producers who produce it use less water and pesticides than in conventional production. IKEA does not apply the principles of sustainability only in our business operations, but we also actively encourage our buyers to live their lives at home in accordance with the principle of sustainable development, and thus in our department stores they can purchase only LED light bulbs, which are compatible with our lightening assortment. We also offer a great number of products which save water, reduce waste etc. For us, the sustainability is not just a responsible attitude towards the environment but also towards the communities in which we operate. We implement a huge number of programs that are largely focused on the improvement of living conditions for children and families who live in difficult circumstances and who are affected by consequences of natural disasters or war conflicts. Just last year, the IKEA Foundation invested 104 million euros in these programs.
EP: What does the production process in IKEA’s factories look like? Do you use renewable energy sources? Do you obtain electricity through solar panels? Can you describe to us standards which are respected in the operation of this company?
 Irena Dobosz: The IKEA company is dedicated to performing business in accordance with the sustainability principles which are grounded on the strategy “IKEA People & Planet positive“. The planning of our investments in the construction of buildings, whether commercial, business or manufacturing are in accordance with this strategy. We have invested 1,5 billion euros in our own renewable energy sources (solar power plants, wind generators) from 2009. Our goal is to achieve energy independency by 2020 by that is to produce the amount of energy that we consume. So far we have installed 700,000 solar panels on our department stores and other facilities world-wide. Numerous standards regulate technical solutions which will be implemented on our facilities. In addition to the construction of our own renewable energy resources (solar power plants on the roof of the facilities or the usage of geothermal energy), other key principles applied are the rational consumption of energy and resources through the application of new materials and technologies (for example LED lightening in the facilities, the use of sophisticated systems for planning and facility management, etc.), the use of renewable materials and waste management.
Irena Dobosz: The IKEA company is dedicated to performing business in accordance with the sustainability principles which are grounded on the strategy “IKEA People & Planet positive“. The planning of our investments in the construction of buildings, whether commercial, business or manufacturing are in accordance with this strategy. We have invested 1,5 billion euros in our own renewable energy sources (solar power plants, wind generators) from 2009. Our goal is to achieve energy independency by 2020 by that is to produce the amount of energy that we consume. So far we have installed 700,000 solar panels on our department stores and other facilities world-wide. Numerous standards regulate technical solutions which will be implemented on our facilities. In addition to the construction of our own renewable energy resources (solar power plants on the roof of the facilities or the usage of geothermal energy), other key principles applied are the rational consumption of energy and resources through the application of new materials and technologies (for example LED lightening in the facilities, the use of sophisticated systems for planning and facility management, etc.), the use of renewable materials and waste management.
EP: IKEA is a Swedish brand, do you follow design and architectural solutions of Sweden and do you take good practice from the countries in which you operate?
Irena Dobozs: Clean, simple, humane would be the key words related to the architecture of the facilities and they also reflect the values on which the company was established. The style can be described as modern functional architecture, which shares the same values. This style is developed from the Swedish modern architecture and functionalist architecture from 1920s and 1930s, which are also by clean geometric forms, without decoration, planned by the principle in which form follows the function.
EP: Can you tell us in how many countries does IKEA operate in and what was the financial balance at the end of 2015?
 Irena Dobosz: IKEA continuously records an increase on a global level. Last year we had an increase of 11% and at the moment there are 375 IKEA department stores in 28 countries, which achieved a turnover of more than 33 billion euros and 884 million visits. With its diverse business activities IKEA is present in 43 countries and the number of employees arose to 172,000 last year.
Irena Dobosz: IKEA continuously records an increase on a global level. Last year we had an increase of 11% and at the moment there are 375 IKEA department stores in 28 countries, which achieved a turnover of more than 33 billion euros and 884 million visits. With its diverse business activities IKEA is present in 43 countries and the number of employees arose to 172,000 last year.
Interview by: Vesna Vukajlović










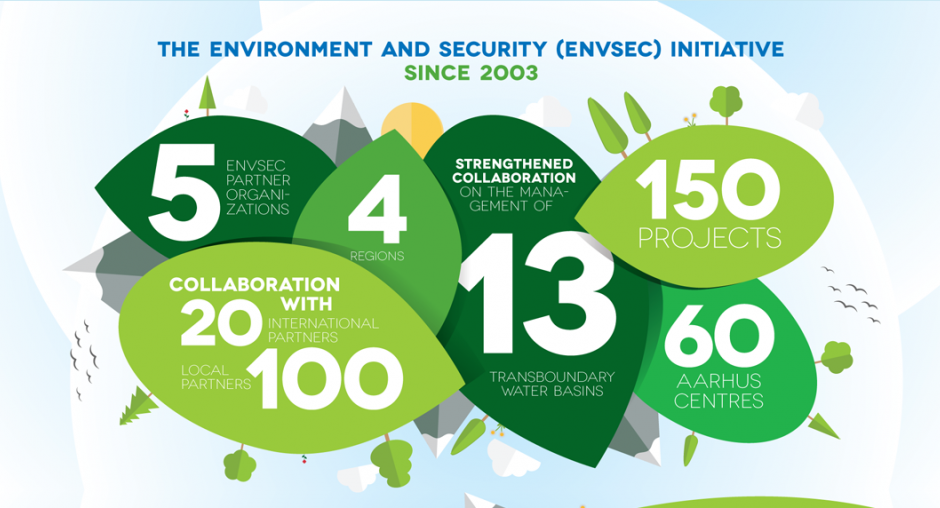
 The Environment and Security Initiative (ENVSEC) stakeholders discussed on 9th June in Batumi how the Initiative can contribute to the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and transition to green economy at an ENVSEC side event on the occasion of the Eighth Environment for Europe Ministerial Conference.
The Environment and Security Initiative (ENVSEC) stakeholders discussed on 9th June in Batumi how the Initiative can contribute to the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and transition to green economy at an ENVSEC side event on the occasion of the Eighth Environment for Europe Ministerial Conference.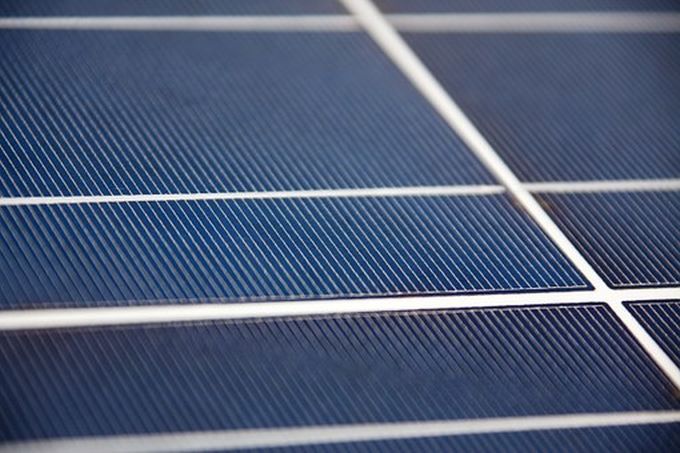














 Matola Gare, Mozambique is now home to a new $130 million world-class bottling plant – the latest milestone in a 10-year, $17 billion investment plan by the Coca-Cola system in Africa.
Matola Gare, Mozambique is now home to a new $130 million world-class bottling plant – the latest milestone in a 10-year, $17 billion investment plan by the Coca-Cola system in Africa.

 How electricity generation from coal in Canada’s most populous province went from 25 percent to zero in just over a decade.
How electricity generation from coal in Canada’s most populous province went from 25 percent to zero in just over a decade.
