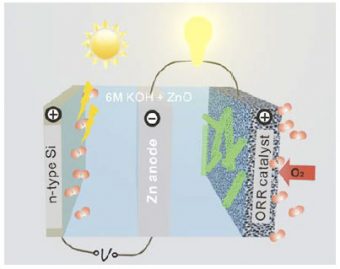
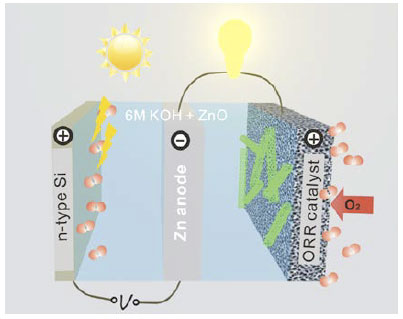
Stanford University scientists have created an advanced zinc-air battery with higher catalytic activity and durability than similar batteries made with platinum and other costly catalysts. The results, published in the journal Nature Communications, could lead to the development of a low-cost alternative to conventional lithium-ion technology widely used today, the researchers said.
“There have been increasing demands for high-performance, inexpensive and safe batteries for portable electronics, electric vehicles and other energy storage applications,” said Hongjie Dai, a professor of chemistry at Stanford and the lead author of the study. “Metal-air batteries offer a possible low-cost solution.”
According to Dai, lithium-ion batteries have attracted the most attention, despite their limited energy density (energy stored per unit volume), high cost and safety problems. “With ample supply of oxygen from the atmosphere, metal-air batteries have drastically higher theoretical energy density than either traditional aqueous batteries or lithium-ion batteries,” he said. “Among them, zinc-air is technically and economically the most viable option.”
Zinc-air batteries generate electricity by combining atmospheric oxygen and zinc metal in a liquid electrolyte, with a byproduct of zinc oxide. When the process is reversed during recharging, oxygen and zinc metal are regenerated.
“Zinc-air batteries are attractive because of the abundance and low cost of zinc metal, as well as the non-flammable nature of the aqueous electrolytes, which make the batteries inherently safe to operate,” Dai said.
“Primary (non-rechargeable) zinc-air batteries have been commercialized for medical and telecommunication applications with limited power density. However, it remains a grand challenge to develop electrically rechargeable batteries, with the stumbling blocks being the lack of efficient and robust air catalysts, as well as the limited cycle life of the zinc electrodes.”
High-performance electrodes are necessary to catalyze the oxygen-reducing reaction during discharge and oxygen production during recharge, he said. In zinc-air batteries, both reactions are sluggish. In recent years, Dai’s group has used nanotechnology to develop novel electrocatalysts with higher catalytic activity and greater durability than conventional electrodes made with platinum, iridium and other precious metals.
For the Nature Communications study, the research team created electrode catalysts made of cobalt oxide, a nickel-iron compound and carbon nanomaterials. “We found that these catalysts greatly boosted battery performance,” Dai said. “We achieved record high-energy efficiency for a zinc-air battery, with a high specific energy density more than twice that of lithium-ion technology.”
The novel battery also demonstrated good reversibility and stability during long charge and discharge cycles over several weeks. “This work could be an important step toward developing practical, rechargeable zinc-air batteries,” Dai said.
Source: news.stanford.edu





 Ball packaging announce recently that 3.5 million cans collected, 2.5 million people reached and 20.000 school-age children educated – with these note-worthy statistics, the Serbian-based recan fund proudly celebrates its 10-year-anniversary. Founded in 2005 by beverage can producer Ball Packaging Europe, the organization is a driving force behind beverage can recycling within the country by using a pioneering approach toward public education and awareness.
Ball packaging announce recently that 3.5 million cans collected, 2.5 million people reached and 20.000 school-age children educated – with these note-worthy statistics, the Serbian-based recan fund proudly celebrates its 10-year-anniversary. Founded in 2005 by beverage can producer Ball Packaging Europe, the organization is a driving force behind beverage can recycling within the country by using a pioneering approach toward public education and awareness.


















 As the planet faces a growing list of problems, from climate change and pollution to environmental degradation and resource depletion, the preservation and conservation of the environment has never been more significant.
As the planet faces a growing list of problems, from climate change and pollution to environmental degradation and resource depletion, the preservation and conservation of the environment has never been more significant.

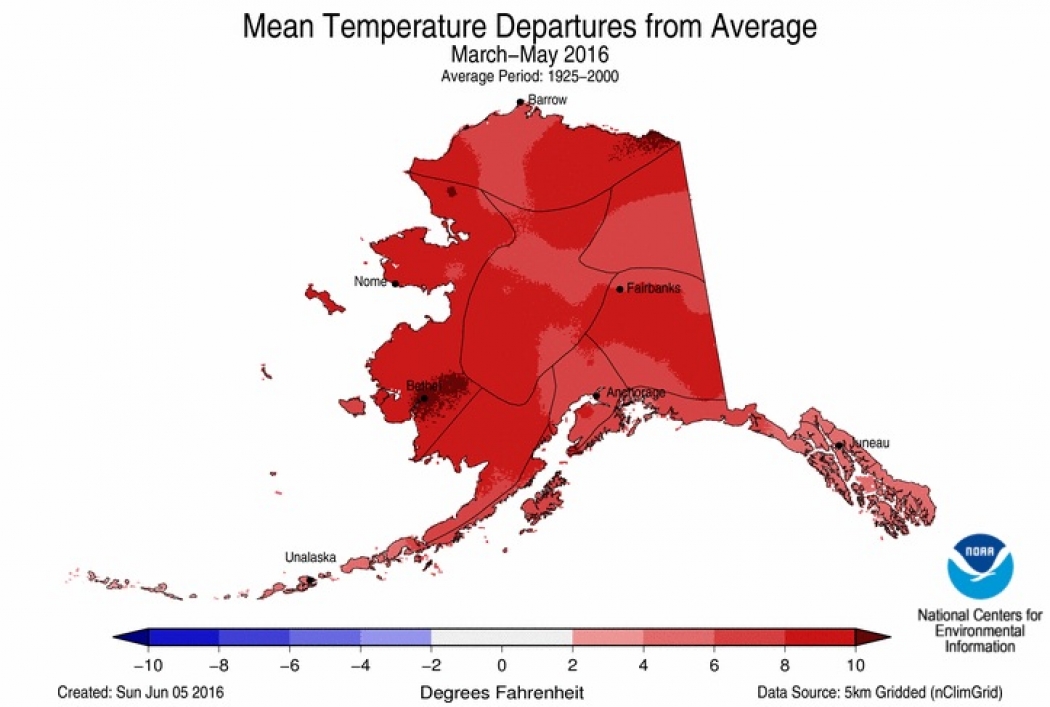
 Alaska just can’t seem to shake the fever it has been running. This spring was easily the hottest the state has ever recorded and it contributed to a year-to-date temperature that is more than 10°F (5.5°C) above average, according to data released by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Alaska just can’t seem to shake the fever it has been running. This spring was easily the hottest the state has ever recorded and it contributed to a year-to-date temperature that is more than 10°F (5.5°C) above average, according to data released by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
