 ABB’s smart sensor, a new condition monitoring solution, connects low-voltage (LV) motors with the twenty-first century. The smart sensor monitors and provides vital motor performance intelligence that helps improve uptime, extend motor lifetimes, and increase machine performance and productivity. It enables motors to be integrated into ABB’s expanding Internet of Things, Services and People (IoTSP) concept.
ABB’s smart sensor, a new condition monitoring solution, connects low-voltage (LV) motors with the twenty-first century. The smart sensor monitors and provides vital motor performance intelligence that helps improve uptime, extend motor lifetimes, and increase machine performance and productivity. It enables motors to be integrated into ABB’s expanding Internet of Things, Services and People (IoTSP) concept.
Up to now it has been too expensive to use permanently installed condition monitoring with LV motors. As a result most LV motors simply run until they fail. ABB’s new smart sensor solution enables almost all LV motors to be remotely monitored. This means that maintenance can be planned in advance, which reduces downtime and saves money. By producing status data for large numbers of motors, the solution also paves the way for plant-wide operations and energy consumption optimization.
The smart sensor solution was developed by ABB together with the Swatch Group, specifically the Swatch subsidiary EM Microelectronic, who developed integrated circuits to read specific measurements. ABB’s smart sensor is a wireless sensor platform consisting of standard as well as jointly developed modules.
Smart sensors fitted to motors

The external sensor monitors signals from the motor. The data is transferred to a secure cloud-based server over the internet. The connection is established using the units’ built-in Bluetooth® via either the user’s smartphone or an ABB gateway solution.
The server analyzes the data and produces meaningful information, which it sends directly to the user’s smartphone or to a dedicated customer portal. Selected ranges of ABB low-voltage motors will be factory fitted with the new smart sensor units as an option. But the smart sensors can also be retrofitted on installed motors.
The intuitive interface includes a simple ‘traffic light’ display to give a quick overview of the plant’s motors. If the system detects a problem that needs attention, it sends an alert to the user’s smartphone. From the portal the user can access trend data as well as data on run time and loads, enabling optimum maintenance planning.
Main benefits
By providing meaningful information on motor condition and performance, the service will enable users to plan their maintenance according to actual needs rather than on the basis of time intervals or operating hours alone. This will reduce maintenance costs and enable the plant to cut or even eliminate unplanned stops. Main benefits of this are increased motor uptime, longer motor lifetime and improved motor performance and productivity. There are also opportunities to optimize motors’ energy consumption – by combining data on the energy consumption levels of individual motors with plant operating information it will be possible to formulate better loading strategies aimed at cutting energy costs.
Taken together, condition and performance data could provide a useful basis for reducing the overall cost of motor ownership in process plants by cutting both the motors’ cost of running as well as the risk and cost of not running.
Monitoring of key parameters
Key parameters that are regularly and accurately monitored are health related information, such as rotor health, temperature, air gap eccentricity, cooling condition, bearing condition and the overall vibration. Also monitored are operating information like energy consumption (within 10%), loading (power) and operating hours. Simple traffic light displays give a quick overview of the motor status. By drilling down the user can identify what triggered a yellow or red signal in order to fix it.
For more information about ABB’s smart sensor visit http://www.abb.com/motorsmartsensor








 In its latest country review of energy policies, the International Energy Agency praised Italy’s comprehensive long-term energy strategy and the acceleration of its efforts to comply with 2020 goals on renewable energy, climate change and energy efficiency.
In its latest country review of energy policies, the International Energy Agency praised Italy’s comprehensive long-term energy strategy and the acceleration of its efforts to comply with 2020 goals on renewable energy, climate change and energy efficiency.
 The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) yesterday announced its 2016 annual enforcement and compliance results, highlighted by a series of high-impact cases that are delivering environmental and public health benefits to communities across the country. During EPA’s 2016 fiscal year—which spanned October 1, 2015 to September 30, 2016—EPA enforcement actions secured $13.7 billion in investments by companies for projects to control pollution. EPA also secured enforceable commitments that ensure the proper treatment, storage and disposal of an estimated 62 billion pounds of hazardous waste, the majority coming through a settlement with Mosaic Fertilizer for their eight facilities across Florida and Louisiana.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) yesterday announced its 2016 annual enforcement and compliance results, highlighted by a series of high-impact cases that are delivering environmental and public health benefits to communities across the country. During EPA’s 2016 fiscal year—which spanned October 1, 2015 to September 30, 2016—EPA enforcement actions secured $13.7 billion in investments by companies for projects to control pollution. EPA also secured enforceable commitments that ensure the proper treatment, storage and disposal of an estimated 62 billion pounds of hazardous waste, the majority coming through a settlement with Mosaic Fertilizer for their eight facilities across Florida and Louisiana.

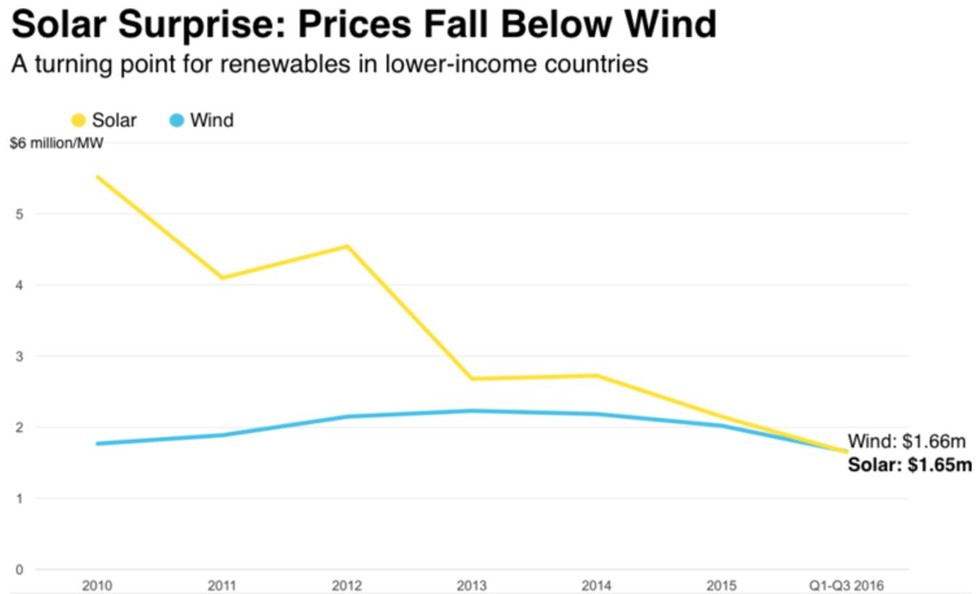





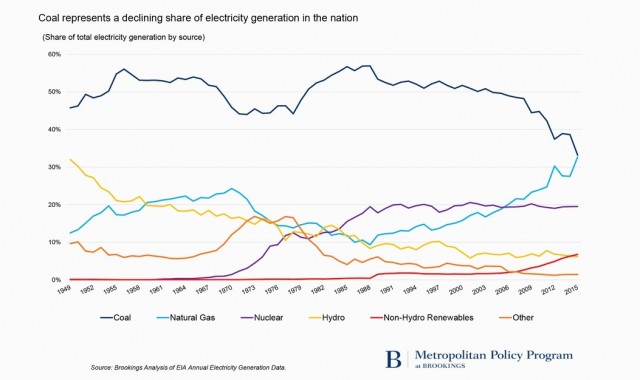
 The coal industry is on the decline, but the reason for that decline has become a subject of political debate. Supporters of fossil fuels blame the energy policies of the outgoing Obama Administration, claiming the emphasis on renewable energy and lowering carbon emissions puts coal at a disadvantage.
The coal industry is on the decline, but the reason for that decline has become a subject of political debate. Supporters of fossil fuels blame the energy policies of the outgoing Obama Administration, claiming the emphasis on renewable energy and lowering carbon emissions puts coal at a disadvantage.




