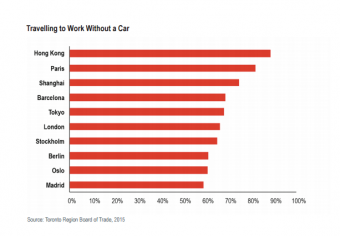
 Nearly 90% of Hong Kong’s residents commute without using a car, while more than 80% of Parisians travel to work on foot, by bike or using public transport, according to research outlined in JLL’s Benchmarking the Future of World Cities report.
Nearly 90% of Hong Kong’s residents commute without using a car, while more than 80% of Parisians travel to work on foot, by bike or using public transport, according to research outlined in JLL’s Benchmarking the Future of World Cities report.
But rapid urbanisation is putting significant strain on infrastructure – affecting both public transport and private car users.
To address the problem, cities – and innovators – are building effective and forward-facing public transport systems. For example, Shanghai has built 21 subway lines, London opened its East-West and North-South cycle ‘superhighways’, and Elon Musk has pioneered a ground-breaking Hyperloop.
Paris, ranked second, has a consistently highly ranked transport system, while Shanghai, in third, already has an extensive subway system, with further expansion planned by 2030.
Seven of the top 10 cities on the list are Western European. The JLL report highlights the strength of public transport systems in not only these major European cities, but also medium-sized ones. “Their size and relative compactness makes systems manageable, affordable and comfortable,” write the report’s authors.
Environmental concerns, including both short-term smog and pollution, and the longer-term contribution of car emissions to climate change, are driving change.
Oslo announced plans last year to ban all vehicles from its center within the next few years. Meanwhile, Paris has already held car-free days, with further initiatives announced this year. Designated routes will be car-free on Sundays and public holidays, while other routes will see cars banned entirely.
By 2020, only cars made in or before 2011 will be allowed in the city.
But ending our love affair with cars won’t be easy. An Australian study showed that “commuters are unlikely to sacrifice the comfort of the private car for a minor time saving”. To encourage more people to use public transport, we’ll need to break this emotional attachment to the car, argues the author. At the same time, breakthroughs in electric car technology also offer hope for cleaner commutes.
Source: weforum.org




 The basis of socially responsible functioning of each company is the fact that it becomes aware of the importance and necessity of its own impact on improving general social conditions and the environment in which it operates. This is the reason why the energy efficiency has become a permanent commitment and strategic scheme of the Atlantic Group to reduce the impact on the environment through the rationalization of energy and water consumption, decreasing of waste and increasing of waste separation, generally in all our processes.
The basis of socially responsible functioning of each company is the fact that it becomes aware of the importance and necessity of its own impact on improving general social conditions and the environment in which it operates. This is the reason why the energy efficiency has become a permanent commitment and strategic scheme of the Atlantic Group to reduce the impact on the environment through the rationalization of energy and water consumption, decreasing of waste and increasing of waste separation, generally in all our processes.