 Many countries use fossil-fuel subsidies to advance particular goals – whether political, economic, social and environmental. Common justifications range from reducing energy poverty, redistributing wealth, or protecting jobs.
Many countries use fossil-fuel subsidies to advance particular goals – whether political, economic, social and environmental. Common justifications range from reducing energy poverty, redistributing wealth, or protecting jobs.
But in many cases, the net effects of fossil fuel subsidies are negative. In practice, subsidies introduced for social reasons, such as price controls on household fuels or support for coal mining to protect jobs, often carry large financial, economic and environmental costs.
In Indonesia, the consequences of persistent under-pricing of energy have been acutely felt. Thanks to low energy prices, rising incomes and low interest rates for vehicle loans, the demand for vehicles – mainly cars and motorcycles – has grown rapidly over the past decade. Transportation accounts for nearly all of the subsidised fossil-fuel consumption.
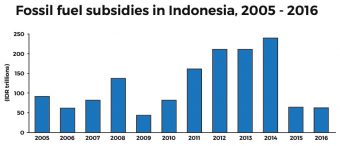
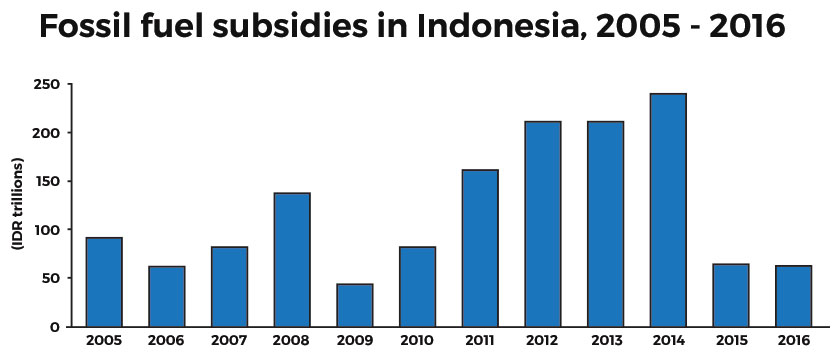
But Indonesia is taking action. The so-called “big bang” removal of subsidies in early 2015, along with efforts to target remaining subsidies to poor households and low oil prices, have been successful in significantly reducing the amount of subsidies. Spending on fossil fuel subsidies in 2016 is projected to amount to less than 1% of GDP, versus more than 3% in 2014.
Fossil fuel subsidies are not new in Indonesia. Subsidies were introduced around the time of independence in 1949 and by the 1960s accounted for nearly 20% of fiscal expenditure. The sharp devaluation of the currency during the Asian crisis of the late 1990s further ratcheted up their cost. By 2014, the economic value of fossil fuel subsidies in Indonesia amounted to $27.7 billion.
One consequence, immediately visible in the capital Jakarta, is chronic congestion. This comes with its own costs, including air pollution, negative health effects and reduced productivity. All this creates additional carbon emissions and undermines progress towards the government’s ambitious carbon emission goals.
But the partial removal of subsidies has yet to be fully implemented. Progress has been hampered by opposition to change from entrenched interests – a mix of household consumers, industry and trade lobbies.
IEA analysis has shown that the best way for policies to succeed involves a fully-fledged political and communications strategy that sets out the costs of subsidies and the benefits of savings to other sectors that will directly benefit citizens. Along with opinion surveys, focus groups and other discussion forums, the government can identify changes to expenditure that are widely supported. Finally, Indonesia can remove the link between social assistance programmes and energy pricing and policy, implementing more targeted social programmes.
The government of Indonesia has until recently, struggled to develop convincing political narratives for reform. For the sake of the economy and the environment, this may now be changing.
Source: iea.org















 Nestlé Waters & Groupe E GreenWatt have just inaugurated the largest agricultural biogas plant in Switzerland, located next to the Henniez bottling plant. This initiative represents a further step in the Eco-Broye program launched by Nestlé Waters in 2009. The Eco-Broye program preserves biodiversity and natural resources ensuring the protection of 100 hectares around Henniez’ site.
Nestlé Waters & Groupe E GreenWatt have just inaugurated the largest agricultural biogas plant in Switzerland, located next to the Henniez bottling plant. This initiative represents a further step in the Eco-Broye program launched by Nestlé Waters in 2009. The Eco-Broye program preserves biodiversity and natural resources ensuring the protection of 100 hectares around Henniez’ site.




 Shell has signed an agreement with Vitol Africa B.V. to sell its 20% shareholding in Vivo Energy for US$250 million. Completion of this transaction is expected during the first half of 2017, subject to regulatory approval. The sale is in line with Shell’s strategy to concentrate its Downstream operations where it can be most competitive.
Shell has signed an agreement with Vitol Africa B.V. to sell its 20% shareholding in Vivo Energy for US$250 million. Completion of this transaction is expected during the first half of 2017, subject to regulatory approval. The sale is in line with Shell’s strategy to concentrate its Downstream operations where it can be most competitive.






