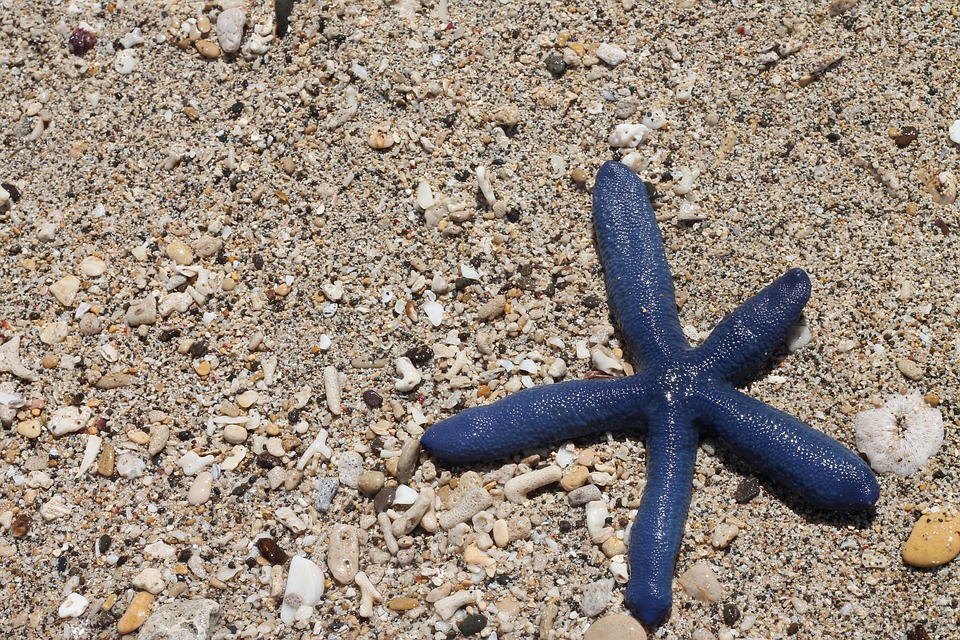
In the summer of 2013, the ocher sea stars of the California coast fell victim to a deadly plague.

First they developed ominous white patches. Then, in a touch straight from a horror movie, their rotting arms began to detach from their bodies and crawl away. They didn’t make it far.
“They just kind of dissolve within days,” said Lauren Schiebelhut, a biologist at the University of California, Merced, who studies the creatures.
More than 80 percent of the ocher sea stars on the northern coast died as a result of that outbreak of sea star wasting syndrome, as the disease is called. In the wake of the devastation, Dr. Schiebelhut and her colleagues looked at the survivors and wondered: Did they have something that the dead did not?
In a new paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, they report a detectable difference between the genes of sea stars before the epidemic and the survivors. Genetic tests also show that new generations of sea stars have more in common with the survivors than with past generations — the events of 2013 seem to have left an indelible mark on the sea star’s gene pool.
The ocher sea star makes its home in rocky tide pools all along the California coast. Before the outbreak, the researchers had taken tissue samples at 16 different locations scattered between the San Francisco Bay and the Oregon border. Afterward, they took samples from the survivors in the same locations. Using several kinds of genetic testing, they found that some sequences were more common in sea stars now than they had been before, while others were less common.
Then, they turned their attention to the juvenile sea stars that appeared after the outbreak.
Each year, flurries of tiny sea star larvae spend the first stage of their life floating in the open ocean. Months later, they return home to settle down.
At the time of the wasting disease outbreak — the cause of which is still unknown, but may be linked to warmer temperatures — many larvae spawned by dying sea stars were still at sea. The researchers thought that when the next batch of young sea stars appeared, they would resemble previous generations. “We expected their gene pool to look very similar to the original adults,” said Dr. Schiebelhut.
Source: The New York Times