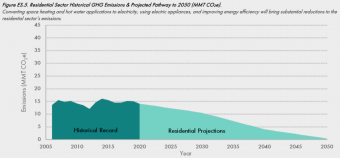
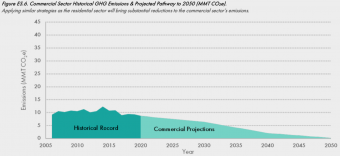
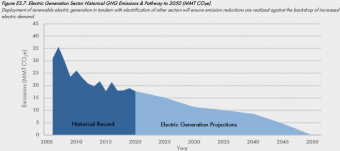
Cities have always had to conform to their natural surroundings. Traditional Moroccan housing was designed with open air courtyards to help with ventilation in the dry and hot climate. While in Iceland, turf houses covered in grass— the original “green buildings”— offered superior insulation in cold weather compared to those made only of wood or stone.
Nature-based solutions have played a crucial role in cities’ design for centuries, but rapid urbanization is putting natural resources to the test.
The UN estimates that over the next 30 years, an additional 2.4 billion people are likely to live in urban areas, 68 percent of the global population in 2050, with most of this shift occurring in the global south. Currently, a third of city inhabitants are estimated to live in slums and informal settlements, often without access to proper housing and basic services. Poor and unplanned urbanization impact resource use, biodiversity and climate.
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) cities’ unit is releasing a new set of guidelines for policymakers and city practitioners for integrated and sustainable neighbourhood design with an emphasis on community needs. These guidelines aim at guiding policy development and practical application in new developments and in the regeneration of existing neighbourhoods.
“Sustainable cities and communities start with sustainable neighbourhoods,” said Martina Otto, head of the cities’ unit at UNEP. “By emphasising the importance of local context, design and integration, we aim to inspire stakeholders involved in urban planning to think sustainably about the daily needs of people in their neighbourhoods. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic and the climate, nature and pollution crisis, reconsidering present urban development paradigms is all the more important and mixed-use, green and interconnected neighbourhoods are a stepping stone for the needed transformation.”
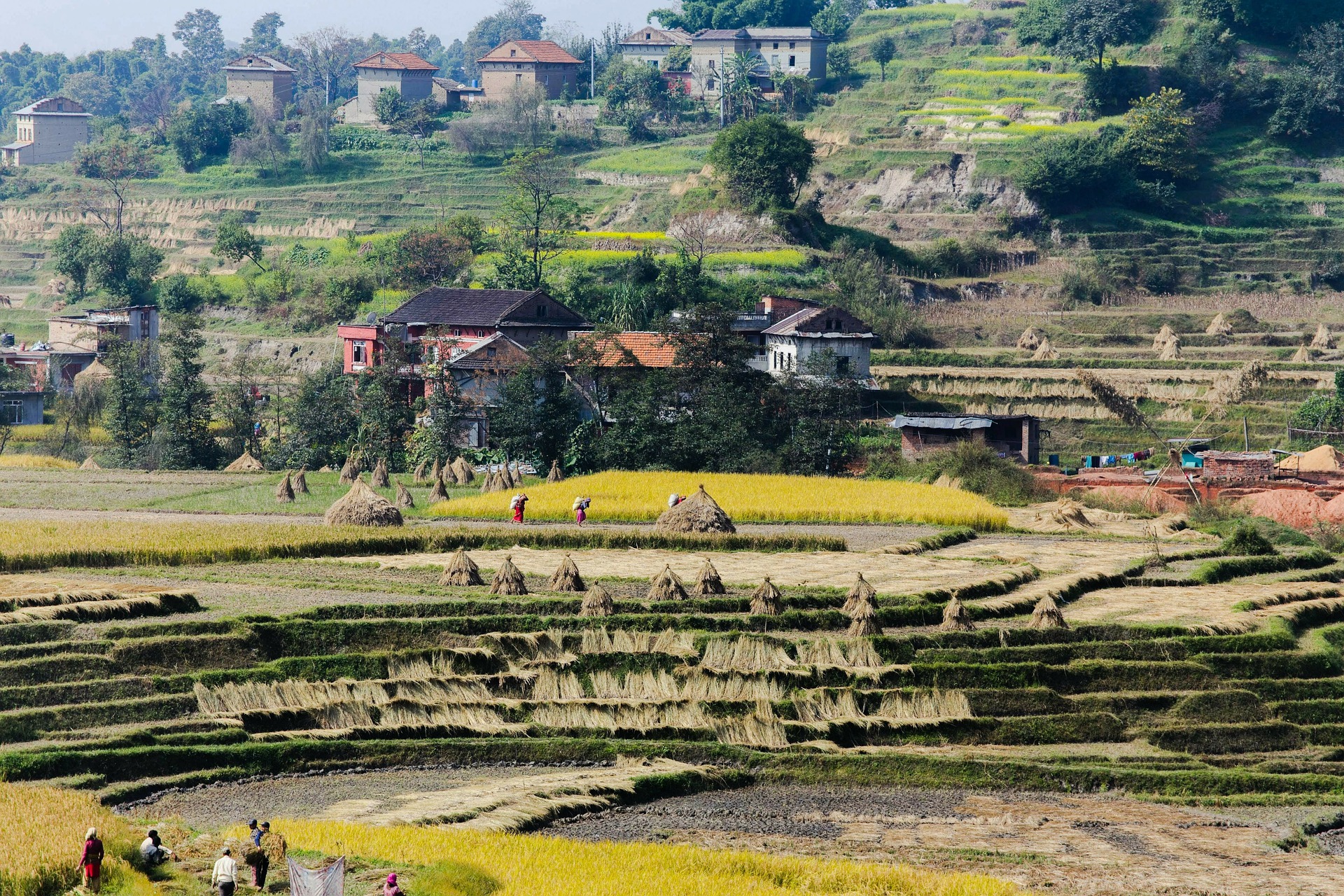
An eco-city in Nepal
One of the cities that UNEP is working with is Lalitpur, in Nepal’s Kathmandu valley. When it was built about 1720 years ago, city planners ensured that open spaces, water availability and ground water recharge were inclusive.
But urbanization and inadequate growth management deteriorated the quality of life in new neighbourhoods. Today, Lalitpur is heavily dependent on fossil fuels, with many residents lacking basic facilities, like water supply and sanitation, and with few green spaces.
UNEP is working with the city government to reinstate Lalitpur as an eco-city. Starting with three neighbourhoods, the consort will construct seven parks, install smart, solar lights; reduce waste to landfill; cut down open burning; and give residents access to health facilities in their neighbourhoods, among other benefits.
More:

“Lalitpur is restoring the resilient and resource-efficient forms of urbanism on the basis of its history and local knowledge, with the goal of becoming a clean and sustainable city,” said Lalitpur Metropolitan City Mayor, Chiri Babu Maharjan. “We have built 4.7 km of bicycle lanes to link the northern and southern parts of the city, and installed bicycle stands in the historic Patan Durbar Square. Thanks to this, the air pollution in the city center has greatly improved, and with that, the health and well-being of our citizens.”
On the move in Medellin
UNEP is also working with the city of Medellin in Colombia on the neighbourhood of Moravian the 1960s, millions of internally displaced Colombians set up homes in Moravia, which at the time held the municipal landfill site. The living conditions were dangerous and many residents suffered serious health consequences from the toxic fumes.
While the neighbourhood has made many advances in sanitation and urban planning since then, city authorities are determined to do more. Medellin is establishing “habitat and mobility corridors” that will simultaneously address mobility issues while creating green spaces and biodiversity. The corridors will be pathways for cyclists and pedestrians to access recreational places such as the local soccer field and cultural centres, but also provide habitats for native animals and plants. They should also have a positive impact on the microclimate by reducing heat and creating shade.
“Neighbourhoods are windows for immediate action,” said André Confiado, who works on Sustainable Cities for UNEP. “They are big enough to bundle interrelated components and give way to a coherent urban fragment, yet small enough to achieve results in a foreseeable time period. The approaches suggested in UNEP’s Integrated Guidelines for Sustainable Neighbourhood Design, and the training we propose to participating cities will contribute to the Global Environment Facility funded Sustainable Cities Impact Programme”.
Source: UNEP