The project „EU for Natura 2000 in Serbia” organised in collaboration with the Energy Portal a photo contest „Natura 2000 in the frame” from September to November 2020.
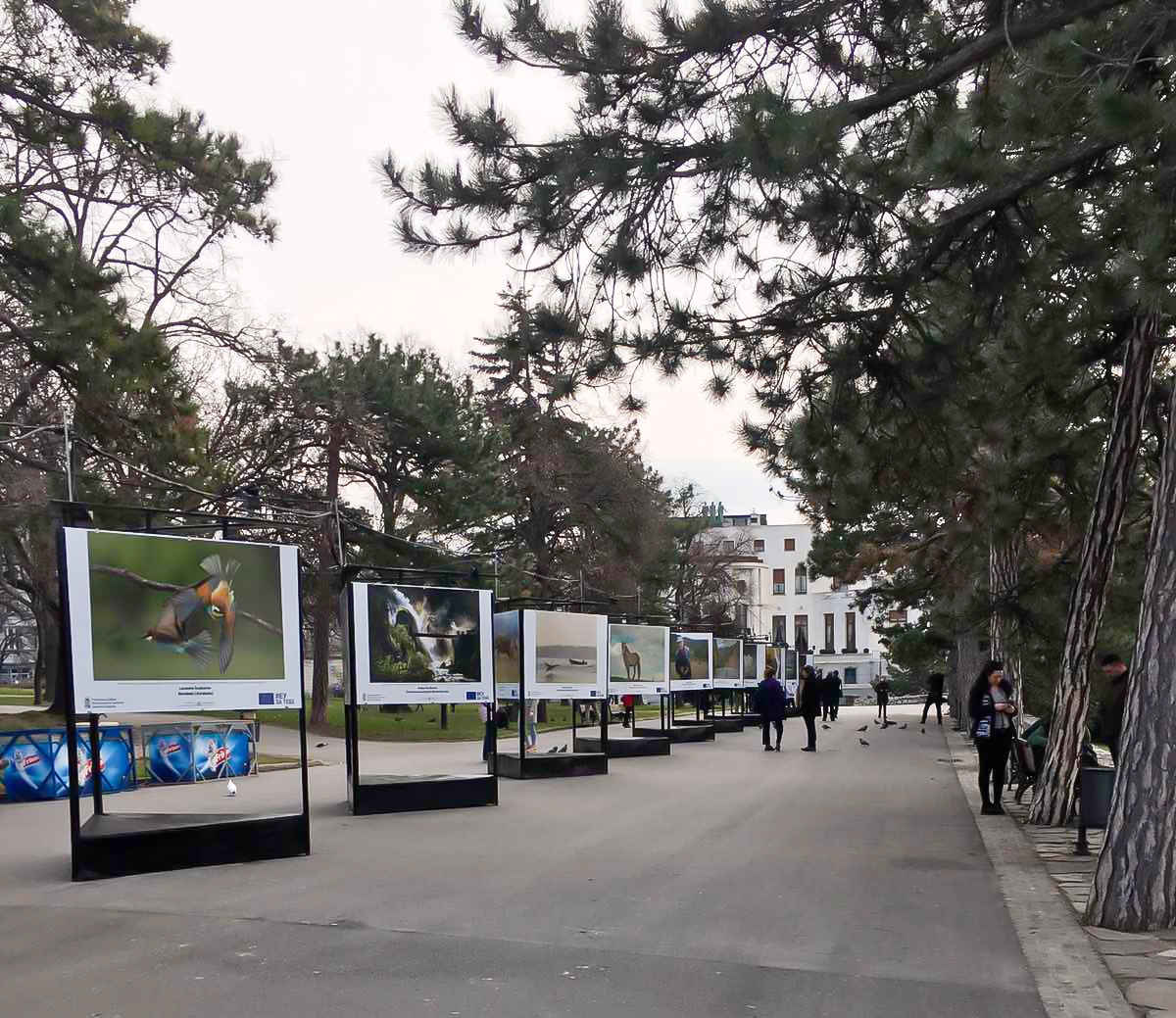
Out of more than 1,500 received photographs, three winning and 31 best semi-finalist photographs were selected and are displayed at an outdoor photo exhibition at Kalemegdan Fortress during March and April 2021.
This exhibition aims to show through these amazing photographs the important biodiversity values and beautiful landscapes in Serbia, as well as raise public awareness of the importance of nature conservation, diversity of flora and fauna, and benefits of the Natura 2000 network for Serbia.
The main topics to which amateur and professional photographers responded were: protected areas and landscapes, natural beauties, Serbian flora and fauna and, sustainable human activities.
It is essential to connect the importance of protection of biodiversity with the diversity of natural landscapes in Serbia, highlighting the sites that will be part of the Natura 2000 network, and to show during a walk through Kalemegdan the beautiful landscapes in Serbia, motivating and reminding citizens about the importance of protection of the environment and the diversity of flora and fauna that they can admire in the country.
More:
“The participants in the competition noticed beautiful landscapes with their lenses and thus reminded us of the natural resources that Serbia has. The exhibition we opened today is part of an EU project that deals with the identification of species and habitats that will be part of the Natura 2000 network. In the Ministry I lead, in preparation for Chapter 27, which deals with the environmental protection and climate change, we are working to improve the implementation of EU regulations for this important area, which relates to nature protection. We also have an important job ahead of us in strengthening the capacity of institutions for the implementation of the Habitats and Birds Directives and the establishment of the European ecological network Natura 2000 in Serbia”, said the Minister of Environmental Protection, Irena Vujovic.

The Natura 2000 network is a crucial instrument for biodiversity protection in the European Union, an ecological network of protected areas established to secure the survival of the most valuable species and habitats, ensuring that European nature systems stay healthy and resilient. The EU is supporting the Ministry of Environmental Protection in the establishment of the Natura 2000 network in Serbia through the project “EU for Natura 2000 in Serbia”.
H.E. Ambassador and Head of the EU Delegation to Serbia Sem Fabrizi expressed his congratulations to the talented Serbian photographers who have captured digitally the important biodiversity values and beautiful landscapes of Serbia.
“It is also the occasion today to mark the World Wildlife Day, when we are remembered how remarkable wildlife is: from small invertebrates to big mammals, they are crucial for the proper functioning and maintenance of ecosystems, and thus for ourselves. Serbia is part of the world and part of Europe, and has its role to play in protecting the important biodiversity values and landscapes. To ensure the long survival of them is a responsibility of all the citizens and the EU is with Serbia for this”, said Ambassador Fabrizi.
The project has a focus on research and monitoring the most important species and habitats. Serbia is very rich in terms of biodiversity, with around 43 percent of the European species present in the country. Serbia’s territory is characterised by fantastic genetic, species and ecosystem diversity, although species diversity is in the process of being fully researched and documented. Approximately 44,200 species and subspecies have been registered so far, and the total number of taxa is estimated at 60,000.
The opening of the photo exhibition marks the World Wild Animal Day 2021, to celebrate the signature of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora. In 2021, the theme is “Forests and Livelihoods: Sustaining People and Planet”, as a way to highlight the central role of forests, forest species and ecosystems services in sustaining the livelihoods of hundreds of millions of people globally.
The exhibition “Natura 2000 in the frame” will be held on the Kalemegdan fortress from March 5th till April 2021.
Source: Natura 2000