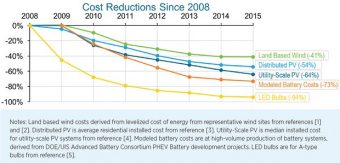
 A new report from the US Department of Energy paints a bright picture for our prospects to cut carbon pollution and prevent the most dangerous levels of climate change. The report looked at recent changes in costs and deployment of five key clean energy technologies: wind, residential solar, utility-scale solar, batteries, and LED bulbs. For each technology, costs fell between 41% and 94% from 2008 to 2015.
A new report from the US Department of Energy paints a bright picture for our prospects to cut carbon pollution and prevent the most dangerous levels of climate change. The report looked at recent changes in costs and deployment of five key clean energy technologies: wind, residential solar, utility-scale solar, batteries, and LED bulbs. For each technology, costs fell between 41% and 94% from 2008 to 2015.
The report finds that due to its low cost, US wind energy capacity has nearly tripled since 2008. Wind now supplies nearly 5% of total US electricity generation.
As a result, there are now nearly 90,000 U.S. manufacturing, construction, and wind operations jobs. Research has resulted in bigger turbines that can generate more electricity.
Offshore wind also presents tremendous untapped potential, with the first such project set to begin generating power off the cost of Rhode Island this month. The DOE envisions wind generating 20% of the nation’s electricity by 2030 and 35% by 2050, with costs falling a further 35% by 2050.
Utility-scale solar farm costs have fallen 64% since 2008, and distributed (mostly residential) solar costs by 54%. While solar still accounts for a relatively small percentage of overall US electricity generation, its deployment has been increasing rapidly as costs have dropped. Even the military is getting on board.
In 2015, the solar sector employed about 220,000 Americans. The DOE envisions that solar power could supply 27% of US electricity generation by 2050. Solar deployment is surging in 2016, with around 10 gigawatts (GW) set to be installed this year – equal to all the solar capacity installed in the US through 2014.
Solar panel leasing from companies like Solar City and Sungevity has revolutionized the distributed solar market, accounting for the majority of domestic residential system installed in leading state markets in 2015. This approach makes solar panels obtainable for households that can’t afford to purchase them. Distributed solar costs are expected to fall a further 16–33% by 2020.
The best available LED bulbs use 85% less energy than incandescent bulbs. Although their high efficiency slashes electric bills, the bulbs’ high cost was initially a deterrent to many consumers. However, LED costs have plummeted 94% since 2008. From 2014 to 2015, LED installations in the US more than doubled, and already account for 6% of installed A-type lightbulbs, as well as 11% and 21% of directional bulbs and outdoor lighting fixtures, respectively.
By 2035, DOE anticipates that LEDs will account for 85% of American’s lighting installations, saving Americans nearly $630 billion in avoided energy costs.
Electric vehicle (EV) sales in the US reached 115,000 in 2015, more than double the number sold in 2012. Overall US EV sales will surpass a half-million by the end of this year. As shown by a new paper and app from MIT, EVs reduce greenhouse gas emissions 58% compared to gasoline-powered cars, and often cost less on a per-mile basis. As low-carbon energy deployment increases, EVs will only become cleaner.
The technology is advancing rapidly due to heavy research, with batteries produced at high-volume now costing 79% less than they did in 2009. Chevroletand Tesla will soon release electric cars with 200 mile-per-charge range and before-rebate prices under $40,000, and Renault beat both automakers to the punch with the 250-mile, $28,000 Zoe. There are now more than 35,000 public and private EV charging outlets in the United States, and in the UK, EV charging stations will outnumber petrol stations by 2020.
The MIT study showed that in order to meet climate targets, we need a transition to EV transportation fueled by low-carbon sources of electricity. The DOE report shows that this sort of high-tech clean future is entire plausible; we’re moving in the right direction with falling costs and rising deployment of the right technologies.
Source: theguardian.com



